
New “Bone Glue” Can Heal Fractures in 3 Minutes: If you’ve ever broken a bone—or even sprained something bad enough to earn a trip to the ER—you know the drill: X-rays, long waits, metal plates, screws, and months of healing. But now, scientists in China have developed a breakthrough that sounds straight out of a superhero movie. It’s called “Bone-02”, often referred to as bone glue, and it can heal fractures in just three minutes. Instead of surgeons drilling metal into bones, they apply this special glue that hardens quickly, holds fractured pieces firmly in place, and naturally dissolves as the bone heals. Early reports suggest this innovation could replace metal implants in many surgeries—a game-changer for both patients and healthcare professionals.
Table of Contents
New “Bone Glue” Can Heal Fractures in 3 Minutes
The arrival of Bone-02 “bone glue” could mark the start of a new era in orthopedic medicine—one where bones heal faster, patients recover sooner, and metal implants become a thing of the past. Inspired by nature and powered by cutting-edge science, this innovation blends the best of biology and technology. While more research and FDA approval are still required, the progress so far is undeniable. Bone-02 isn’t just a medical invention—it’s a glimpse into the future of healing.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Technology Name | Bone-02 (“Bone Glue”) |
| Developed By | Dr. Lin Xianfeng, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang Province, China |
| Healing Time | 3 minutes to set |
| Composition | Oyster-inspired bioabsorbable polymer adhesive |
| Bonding Strength | 400+ lbs (≈ 181 kg); 0.5 MPa shear strength |
| Compressive Strength | ≈ 10 MPa (similar to natural bone) |
| Patients Tested | 150+ clinical participants |
| Absorption Time | Naturally dissolves within ~6 months |
| Potential U.S. Impact | Awaiting FDA trials |
| Official Source | Times of India – Bone-02 Report |
What Is Bone Glue and How Does It Work?
Bone-02 is a biomedical adhesive engineered to bond fractured bones together quickly and safely. Inspired by oysters—yes, the same shellfish on your dinner plate—scientists mimicked the way oysters cling to rocks underwater. These creatures secrete a protein-based adhesive that remains strong even in wet environments. The researchers replicated this concept using biocompatible polymers and calcium-based minerals that can bond directly to wet bone tissue.
The result is a glue that sets in under three minutes, holds with remarkable strength, and then gradually dissolves as the bone regenerates. Unlike metal plates that often require a second surgery for removal, this adhesive disappears naturally, leaving behind healthy, healed bone.
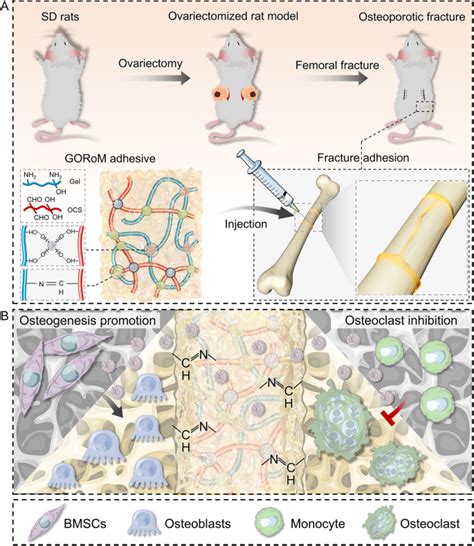
The Science Behind the New “Bone Glue” Can Heal Fractures in 3 Minutes
The success of Bone-02 comes down to chemistry and biology working hand in hand. The material uses a two-part reaction process:
- Activation Phase: When the adhesive is applied to the bone surface, chemical catalysts trigger immediate polymerization—meaning the glue begins to harden.
- Cross-Linking Phase: The adhesive’s polymer chains interlock, forming an incredibly tough yet flexible matrix that can tolerate blood and moisture.
- Integration Phase: The glue’s structure mimics bone’s mineral composition, allowing new bone cells (osteoblasts) to grow into the material as healing begins.
- Degradation Phase: Over roughly six months, the adhesive safely biodegrades into harmless compounds that the body naturally absorbs.
What’s truly fascinating is that this entire process happens while maintaining shear strength of 0.5 MPa and compressive strength of around 10 MPa—strong enough to handle normal joint stress for small to medium fractures.
Metal Plates vs. Bone Glue: A Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Metal Plates | Bone-02 “Bone Glue” |
|---|---|---|
| Surgery Duration | 60–120 minutes | ~30 minutes |
| Healing Time | 8–12 weeks | 4–8 weeks (estimated) |
| Invasiveness | Requires drilling and screws | Minimal incision, direct application |
| Infection Risk | Moderate | Very low |
| Post-Surgery Pain | Moderate to high | Mild |
| Material Removal | Often needed | None (bioabsorbable) |
| Cost | $3,000–$10,000+ | Expected to be lower |
| FDA Approval | Fully approved | Pending |
| Patient Recovery | Slower, more complications | Faster, less invasive |
Why It’s a Big Deal for Healthcare?
This innovation could transform orthopedic medicine in several ways:
- Shorter Surgeries: Operating room time may be reduced by up to 60%, saving hospitals time and money.
- Fewer Complications: No metal means fewer infections and allergic reactions.
- No Second Surgery: Patients won’t need metal removal procedures months later.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduced hardware and surgical time could lower overall healthcare expenses.
- Better for Kids: Since the glue dissolves naturally, it won’t interfere with bone growth in children.
If Bone-02 passes all regulatory hurdles, it could significantly reduce the physical and financial burden of fracture recovery.
Real-World Results So Far
According to reports, over 150 patients have already been treated using Bone-02 in controlled hospital settings. In one documented case, a patient with a fractured wrist achieved full recovery in under six weeks—half the normal healing period—with no signs of infection or stiffness.
Surgeons also noted a 50% reduction in operation time. For small fractures—such as wrists, clavicles, or ribs—the adhesive held firm through daily activities like lifting objects and typing. These are early findings, but they’ve fueled strong optimism among medical professionals.
Expert Opinions from the Field
Dr. Lin Xianfeng, lead researcher and orthopedic specialist, explained:
“We designed Bone-02 to mimic natural healing rather than override it. It’s not just about bonding bone—it’s about supporting the body’s own regeneration process.”
Dr. Karen Lewis, a senior consultant with the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), added:
“If this material can be verified under global standards, it could revolutionize how we handle bone injuries, especially in outpatient and emergency care.”
Experts at the World Health Organization (WHO) estimate that nearly 178 million fractures occur each year globally. A fast, efficient solution like Bone-02 could drastically improve outcomes for patients worldwide.
The Road to FDA Approval in the U.S.
While Bone-02 is making headlines internationally, it’s not yet available in the United States. Before American surgeons can use it, it must pass rigorous testing and approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
This involves multiple clinical phases to confirm its biocompatibility, strength, degradation safety, and long-term stability. If all goes smoothly, Bone-02 could begin clinical trials in the U.S. within the next few years.
Potential Applications Beyond Fractures
The adhesive isn’t limited to fixing broken arms or legs. Scientists are already exploring Bone-02’s use in:
- Dental surgery, where it could help repair jaw fractures or stabilize implants.
- Spinal fusion, reducing the need for rods and screws.
- Battlefield medicine, enabling rapid fracture repair for soldiers.
- Sports injuries, allowing athletes to return to play sooner.
- 3D-printed bone scaffolds, combining the glue with regenerative materials.
There’s even discussion about its use in space medicine, where medical hardware is limited.
Challenges Ahead
Despite its promise, Bone-02 faces some legitimate challenges:
- Testing on Large Bones: Current studies focus on smaller bones; weight-bearing bones like femurs need further research.
- Regulatory Complexity: Different countries have unique medical device regulations, which may slow adoption.
- Manufacturing Scale: Producing bioadhesive materials consistently and safely is technically demanding.
- Long-Term Data: Full studies are required to confirm safety after years—not months—of implantation.
Still, these are typical hurdles for any groundbreaking technology, and research is progressing steadily.
Practical Takeaways
For patients, this means shorter surgeries, faster healing, and fewer complications in the near future. If you or a family member faces orthopedic surgery, it’s worth asking your doctor about emerging bioadhesive-based treatments.
For medical professionals, it’s time to start learning about biomimetic adhesives and their integration with surgical workflows. Staying ahead of these trends will prepare hospitals for when such technology becomes globally available.
For students and researchers, Bone-02 represents a growing field called biomaterials science, where chemistry, engineering, and biology intersect to create next-generation medical tools.
CICR Highlights Climate-Smart Farming Practices to Address Heat Stress in Cotton: Check Details
6 Zodiac Signs That Never Age; Their Beauty Only Grows Stronger With Time
Meet the Cotton Doctors – A Day with CICR Scientists Solving Farmer Problems
The Future of Fracture Repair
Imagine an ambulance worker or ER doctor fixing a broken bone within minutes—no screws, no plates, no months of metal sitting inside your body. That’s the vision Bone-02 represents. It could also open doors to regenerative bone surgery, where adhesives combine with stem cells to rebuild tissue more completely.
Hospitals around the world are watching closely. If this material proves safe, it could redefine bone repair in the same way lasik changed eye surgery—quick, clean, and life-changing.
















