VA Confirms $3,500+ Monthly Payments: If you’re a veteran or care for someone who served in the U.S. military, this is big news: The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has confirmed that many veterans will receive monthly disability payments exceeding $3,500 in 2025. These payments are crucial financial lifelines for those who sacrificed while serving and who now face disabilities related to their military service. But who exactly qualifies for these payments? And how can veterans check their eligibility? This article breaks it down in a friendly, clear way that even a 10-year-old can follow, while still delivering valuable insights for professionals and veterans alike.
Table of Contents
VA Confirms $3,500+ Monthly Payments
In 2025, the VA continues its commitment to supporting veterans by confirming monthly disability payments over $3,500 for those with major service-connected disabilities. Veterans and those assisting them should stay informed about eligibility, detailed rating processes, recent VA updates, and application steps to maximize benefits. Though navigating VA benefits might seem complex, breaking it into clear sections and understanding key principles ensures veterans get what they deserve fairly and promptly. Veterans have earned these benefits through service, and the VA is here to help deliver them.
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| 2025 Monthly Payment Maximum | Up to $4,544 for 100% disability + dependents |
| Eligibility | Service-connected disabilities with 10%-100% rating |
| Payment Adjustment | 3.3% Cost-of-Living Adjustment (COLA) for 2025 |
| Dependents Impact | Payments increase for spouse, children, or dependent parents |
| Typical Payment Range | $175 to $4,544 monthly, based on disability rating and dependents |
| Official Source | VA Official Site |
What Are VA Disability Payments?
VA disability payments are monthly, tax-free benefits paid to veterans who were injured or developed illnesses because of their military service. These payments help veterans cover medical bills, daily living expenses, therapy costs, and personal care needs.
Think of these payments as the government’s way of recognizing the sacrifices veterans made and helping them live a fuller, more comfortable life despite their service-connected disabilities.
Veterans Affairs defines service-connected disabilities as injuries or health conditions that were caused or worsened by military service. The VA assigns a disability rating to reflect the severity of these conditions, which determines how much monthly compensation a veteran receives.
How Much Can Veterans Expect to Receive?
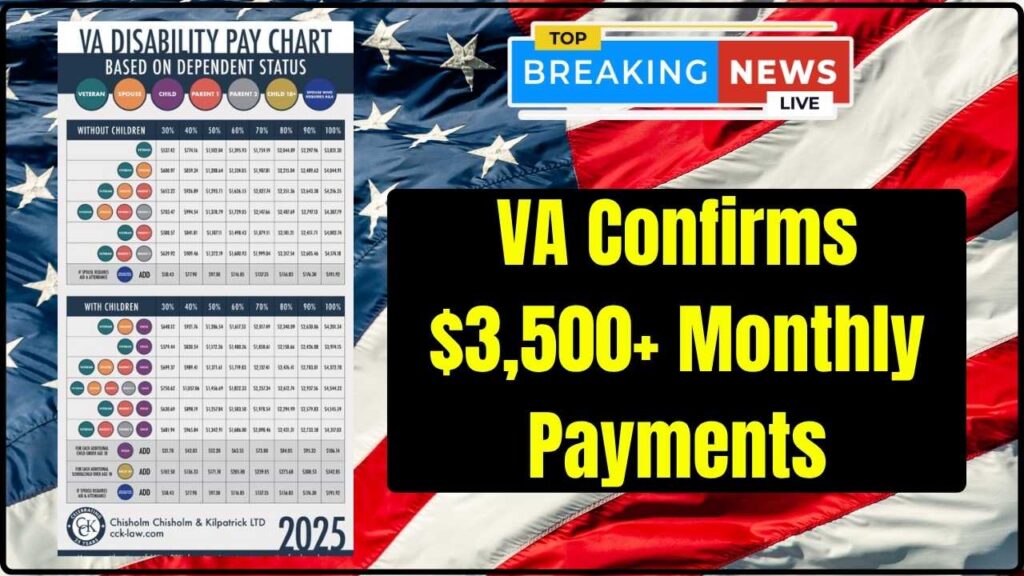
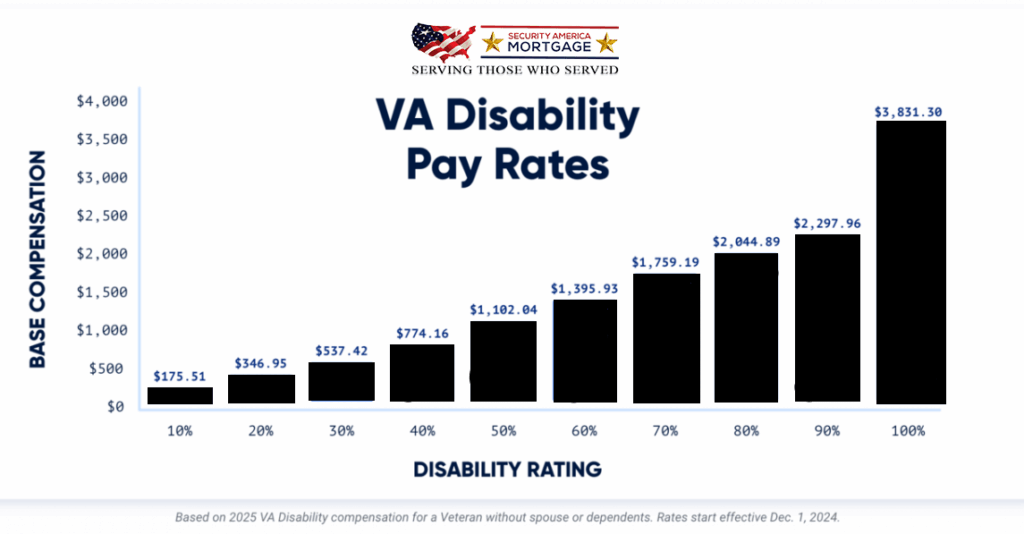
Thanks to a 3.3% cost-of-living adjustment (COLA) for 2025, VA disability payments are at some of their highest levels ever. Here’s a typical breakdown of payments by disability rating:
- 10% disability: Around $175 monthly
- 30% disability: About $537+
- 60% disability: About $1,395+
- 100% disability: Starts at $3,831 for a veteran alone, increasing with dependents
- 100% disability with spouse and child: Can exceed $4,500 monthly
Veterans with very severe disabilities, such as the loss of limbs or those requiring daily personal care, may qualify for additional payments under Special Monthly Compensation (SMC), which boosts monthly income further.
These payments are tax-free federally, providing veterans with more financial stability.
Who Qualifies for VA Confirms $3,500+ Monthly Payments?
Veterans likely to receive payments over $3,500 monthly generally:
- Are rated 100% disabled by the VA based on service-connected injuries or illnesses.
- Have qualifying dependents (spouse, children, dependent parents), which significantly increases payments.
- Are eligible for Special Monthly Compensation (SMC) due to severe disabilities or the need for regular aid and attendance.
- Have combined disabilities rated up to 100%.
Veterans with dishonorable discharges typically are not eligible for these benefits.
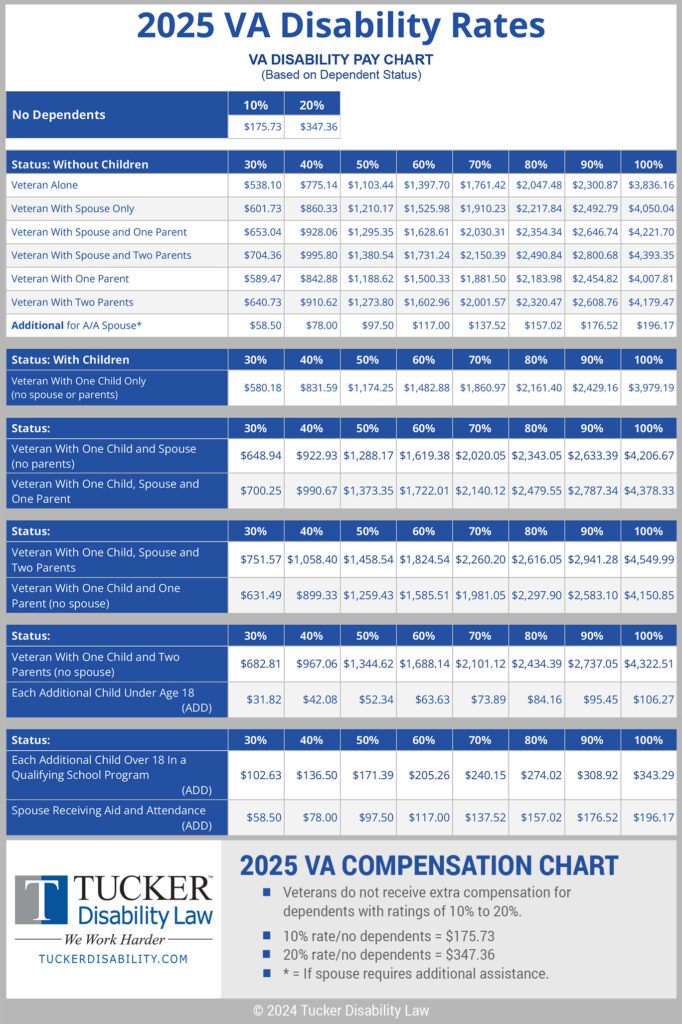
Understanding VA Disability Ratings: A Deeper Dive
The foundation of VA disability payments is the disability rating — a percentage number from 0% to 100% that reflects how much a veteran’s health and functional ability have declined due to service-connected conditions.
How VA Assigns Ratings?
The VA assigns ratings based on:
- Medical evidence: such as doctor’s reports, test results, and medical history.
- Compensation & Pension (C&P) exam: When required, the VA arranges an exam with a physician to assess the severity and impact of the veteran’s disabilities.
Each service-connected condition is assigned its own rating in increments of 10%, ranging from 0% (non-compensable) to 100% (total disability).
Combined Ratings for Multiple Conditions
Many veterans have multiple disabilities. The VA uses a formula called the “whole person theory” to combine ratings without exceeding 100%. This ensures a realistic assessment since a person cannot be more than 100% disabled.
The process begins with the highest individual rating, subtracts that from 100%, then applies subsequent ratings to the remainder. For example:
- A veteran with disabilities rated at 30%, 20%, and 10% will have a combined rating calculated stepwise, not by simply adding to 60%.
Understanding this is crucial, as the combined rating directly determines your compensation.
Examples of Common Disabilities Rated by the VA
- Physical disabilities: limb loss, musculoskeletal injuries, hearing loss, chronic pain.
- Mental health conditions: PTSD, depression, anxiety.
- Chronic illnesses: respiratory disorders, sleep apnea, diabetes, neurological conditions.
The severity impacts both the rating and the compensation amount.
Important 2025 Updates Veterans Should Know
Several key changes in 2025 impact VA benefits:
- Increased Cost-of-Living Adjustment (COLA): The 3.3% COLA helps offset inflation and rising living costs.
- New Rating Criteria: The VA revised how certain conditions are rated, especially mental health disorders, sleep apnea, and tinnitus. For instance, mental health ratings now focus more on symptom severity rather than social impairment.
- Expanded Access to Care: The VA added six new health clinics nationwide to improve veterans’ access to health care services.
- VA Loan Program Reforms: Recent changes aim to protect veterans from foreclosure and homelessness in cases involving VA-backed home loans.
- Digital Service Improvements: The VA now requires more secure authentication methods for online access to benefits, increasing protection against fraud.
These updates mean veterans should stay informed to maximize their benefits.
How Dependents Affect Payments?
Dependents play a major role in increasing VA compensation. Here’s how:
- Spouse: Adds roughly $200+ per month.
- Children: Each child adds more, especially if under 18 or in school.
- Dependent Parents: Additional payments available if you financially support parents.
For example, a 100% rated veteran with a spouse and two kids could qualify for several hundred dollars more monthly compared to a single veteran at the same rating.
How to Check Eligibility and Apply for VA Confirms $3,500+ Monthly Payments
Step 1: Collect Your Records
Gather medical and military service records that prove your condition is service-connected.
Step 2: File Your Claim
Apply using the official VA website or at a local VA office.
Step 3: Attend the C&P Exam
Participate in the Compensation & Pension exam arranged by the VA to assess your condition.
Step 4: Review Your Decision
The VA sends a rating decision letter outlining your assigned disability rating and monthly payment.
Step 5: Appeal if Needed
If you disagree, you can file an appeal or ask for a re-evaluation.
Step 6: Receive Payments
Once approved, monthly payments are made, typically on the last business day.
Veterans should track their claims closely and seek assistance from veterans service organizations if needed.
Common Myths About VA Disability Payments
- Myth: You must be 100% disabled to get payments.
Fact: Veterans rated as low as 10% qualify. - Myth: VA payments are taxable.
Fact: These payments are federally tax-free. - Myth: Only physical injuries count.
Fact: Mental health (like PTSD) and chronic illnesses are compensable.
Additional Benefits Beyond Monthly Payments
Certain veterans qualify for additional allowances:
- Aid and Attendance: Extra money for those needing daily personal care.
- Housebound Allowance: For veterans mostly confined to home.
- Automobile Allowance: Help purchasing a vehicle for disability-related mobility issues.
- Clothing Allowance: For service-connected disabilities requiring medical devices that wear out clothes.
These benefits address specific needs and provide extra financial relief.
60 VA Disability Pay Increase for 2025: See Your New Monthly Payment Amount
VA Disability Pay Chart 2025: See How Much More You’re Getting This Year
$1702 PFD Stimulus Check in November 2025: Know Amount, Eligibility & Payment Dates













