Social Security Boost: If you’re looking to pump up your Social Security monthly payments by hundreds of dollars, you’re in the right place. Social Security is a bedrock of retirement income for millions of Americans, and knowing the right moves can help you get the most out of it. This article breaks down a straightforward strategy alongside other practical tips to help you increase your benefits, all explained in a clear and approachable way. Understanding how to boost your Social Security check doesn’t have to be complicated—whether you’re just starting to plan your retirement or a seasoned pro, this guide’ll get you savvy about your benefits. Let’s dive into what works, what to watch out for, and how you can make your money work harder for you.
Table of Contents
Social Security Boost
Growing your Social Security payments by hundreds of dollars is simpler than you think. By strategically delaying benefits, maximizing your work credits, leveraging spousal and survivor perks, and staying updated on changes like the 2.5% COLA increase in 2025, you can make your retirement income work harder for you. Your Social Security benefits are your earned money—make sure you get the most out of it. Start planning today and keep informed with the Social Security Administration for personalized assistance.

| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Best Strategy to Boost Payments | Delay claiming Social Security until age 70 to earn up to 8% more per year after full retirement age (FRA) |
| Average Monthly Benefit (2025) | $1,976 for retired workers (after 2.5% Cost-of-Living Adjustment) |
| Social Security COLA Increase (2025) | 2.5% increase to adjust for inflation |
| Maximum Taxable Income for Social Security (2025) | $176,100, stepping up from $168,600 in 2024 |
| Spousal Benefits | Up to 50% of the higher earner’s benefit |
| Survivor Benefits | Up to 100% of deceased spouse’s benefit for surviving spouses at full retirement age |
| Official Resource | Visit Social Security Administration for up-to-date info and calculations |
What is Social Security and Why Does It Matter?
Social Security is a government program that provides monthly payments to eligible retirees, disabled persons, and survivors. For many U.S. residents, Social Security is a crucial income source during retirement, helping cover everyday expenses and keep the lights on.
Since it’s a big deal for financial stability, a smart strategy can make a huge difference in what you receive each month. This is especially true because retirement costs keep inching up due to inflation, so you want to make sure your benefits keep pace.
How Are Social Security Benefits Calculated?
Your Social Security benefit is based on your lifetime earnings, indexed to account for inflation. The Social Security Administration (SSA) calculates your Average Indexed Monthly Earnings (AIME) from your highest 35 years of earnings. Then, they apply a formula to this average to get your Primary Insurance Amount (PIA), which is your benefit at full retirement age.
In simple terms, the more you earn over a longer career, the higher your benefit. If you have fewer than 35 years of earnings, zeros are factored in, which lowers your AIME and your benefit.
Social Security Boost
Delay Your Benefits to Earn More
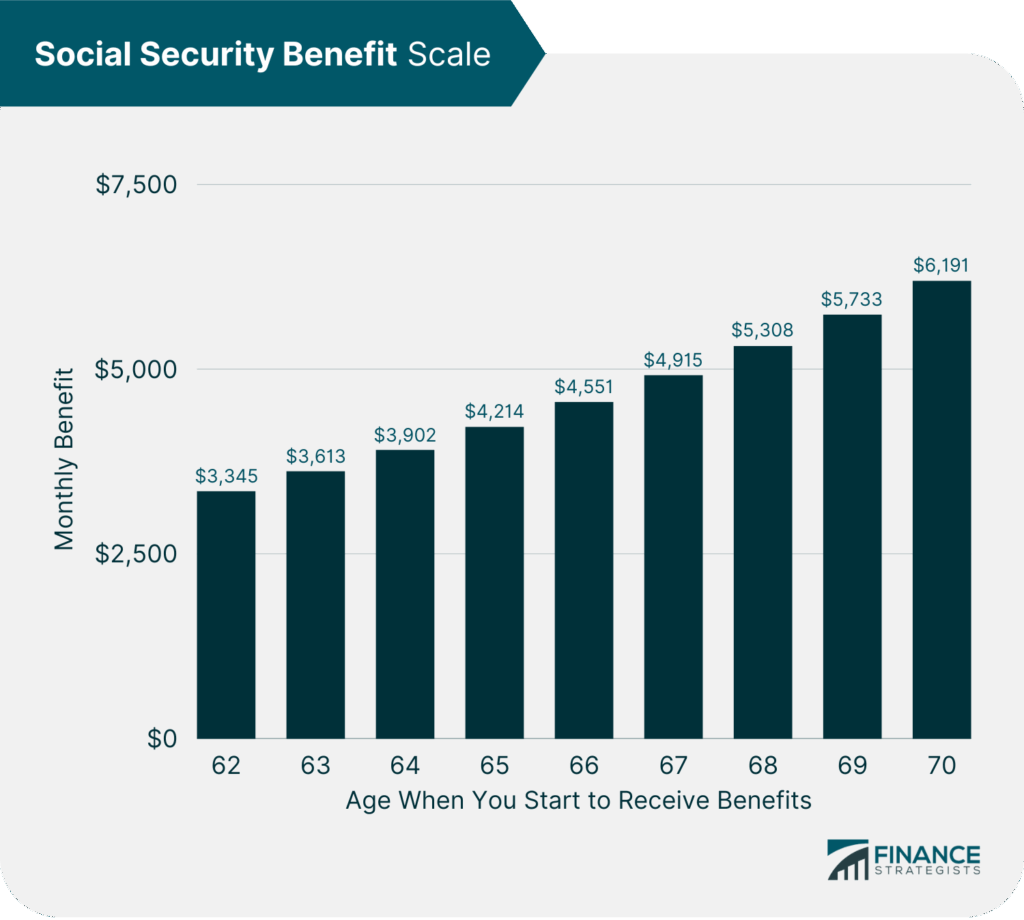
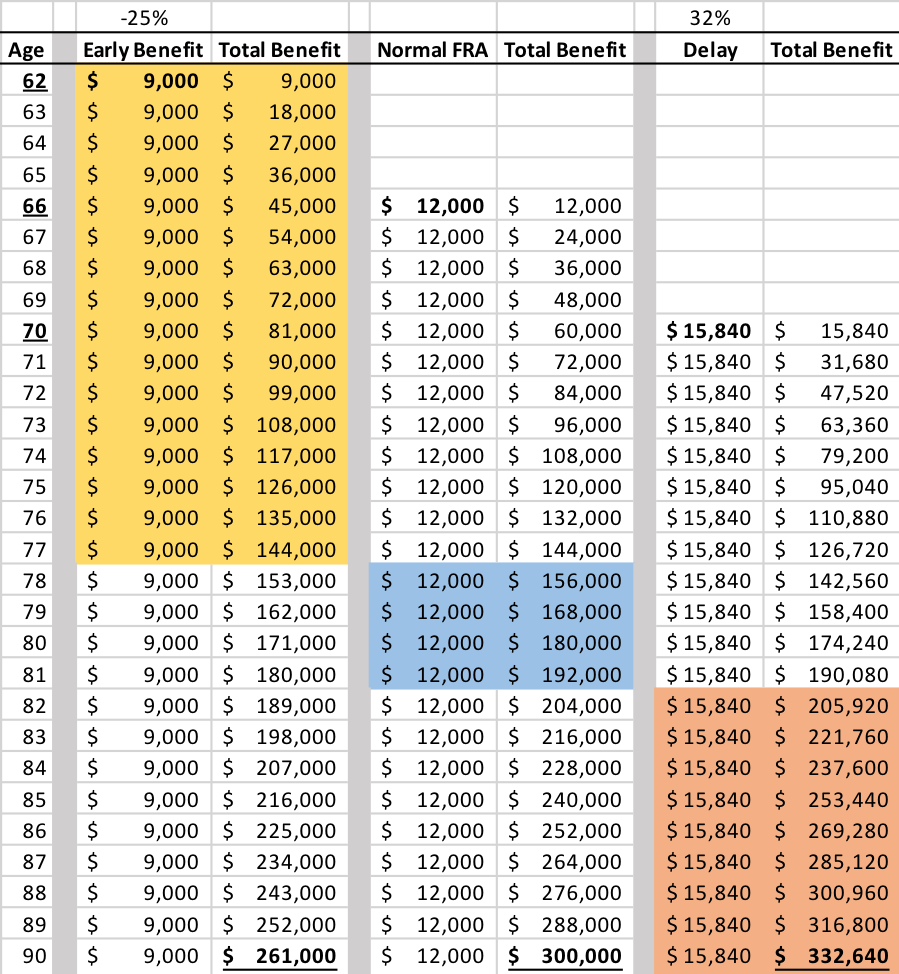
If you start claiming your Social Security benefits before your full retirement age (FRA), your monthly check takes a hit — less money for the rest of your life. But here’s the catch: if you hold off and wait until age 70, you earn delayed retirement credits, which bump up your monthly checks by about 8% each year after your full retirement age.
Example:
- Full Retirement Age: 66 years
- Claim at 66: 100% benefit
- Claim at 70: Up to 132% benefit (8% × 4 years + 100%)
So if your benefit at 66 was $1,000/month, waiting until 70 could boost it to $1,320/month — that’s over $300 extra each month!
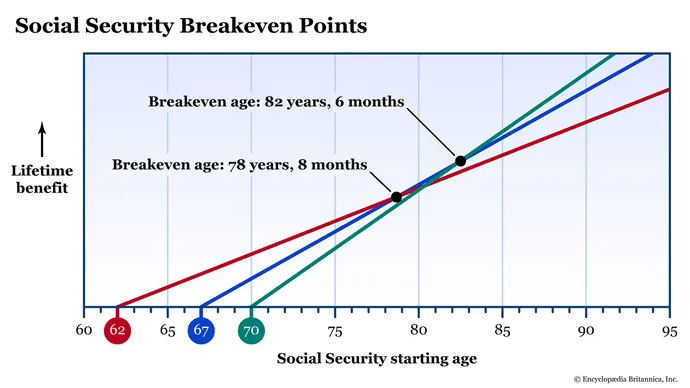
Have a Break-Even Point Strategy
The trade-off with delaying benefits is that you receive nothing for the years you don’t claim. Your break-even age is when the total amount received from waiting catches up to what you would have gotten by claiming earlier. If you live longer than the break-even age, delaying pays off big time.
Most people break even in their late 70s or early 80s, so if you expect to live longer, delaying is a smart bet.
Work Longer and Boost Your Earnings Record
Since benefits are calculated using your top 35 years of earnings, working additional years with good income can replace low-earning years. This helps increase your average and thus your benefit.
Even working after claiming benefits can help if you haven’t reached full retirement age, but there are earning limits to be mindful of — earning too much before your FRA can temporarily reduce your benefits.
Claim Spousal or Survivor Benefits
Married couples have special Social Security rules:
- Spousal benefits let the lower earner claim up to 50% of the higher earner’s benefit.
- Survivor benefits let widows and widowers claim up to 100% of the deceased spouse’s benefit once the survivor reaches full retirement age.
To put it plainly, if your spouse passes away, you could be eligible to receive the full amount of their Social Security benefits, which can be a critical source of income in tough times. Eligibility for survivor benefits typically requires that you were married at least nine months before your spouse’s death, although there are exceptions for accidental death or military duty.
If you care for a child under age 16 or disabled from the deceased marriage, survivor benefits are available at any age, and disabled surviving spouses can collect as early as age 50.
Divorced spouses also qualify for these benefits if they were married for 10 years or longer and haven’t remarried before age 60.
Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) and Supplemental Security Income (SSI)
Not everyone qualifies for retirement benefits right away. SSDI helps those who are disabled and can’t work by providing monthly income based on their prior earnings. SSI offers extra help to low-income elderly or disabled individuals who may not have enough Social Security credits.
Review and Correct Your Earnings Record
Mistakes in your earnings record can lower your benefits. Check your Social Security statement annually to ensure your earnings are correctly reported. If you spot errors, contact the SSA to fix them, as your future monthly check depends heavily on your recorded income history.
Combine Social Security with Other Retirement Income
Social Security is only part of your retirement income. Maximize your security by combining your benefits with other sources like pensions, IRAs, 401(k) plans, and personal savings. Don’t forget Medicare, which generally begins at age 65 and may involve premiums deducted from your Social Security check.
What’s New for Social Security in 2025?
2025 updates include:
- A 2.5% Cost-of-Living Adjustment (COLA) to help benefits keep pace with rising prices.
- The average monthly retired worker benefit is $1,976 for 2025.
- The maximum taxable income for Social Security tax rose to $176,100.
- The Social Security Fairness Act removes some penalties for federal workers, increasing benefits for many.
Step-By-Step Guide to Maximize Your Social Security Boost
- Know your Full Retirement Age (FRA).
- Consider delaying benefits until age 70 to get the highest monthly payments.
- Work enough years (35+) with good earnings to boost your benefit.
- Explore spousal and survivor benefits if you’re married or widowed.
- Regularly check your earnings record for errors and correct them.
- Plan your work and earnings to avoid early claiming penalties.
- Manage taxes on benefits to keep more money in hand.
- Use SSA online tools and consult a financial advisor for personalized planning.
Social Security Payment Changes for Thanksgiving 2025 – Check Payment Amount, Date & Eligibility
$1,978 Social Security Payment expected in October 2025? Check Payment & Claim Process
$2,831 Social Security Payment If You Born in April 1963: How to claim it? Eligibility Criteria!